The individual & company tax rates you should know

Whether you’re an employee, self-employed or run a business, everyone ought to understand their obligations to the taxman.
Knowing your tax rates is essential for financial planning and decision making. Not only will understanding your tax rates ensure you meet compliance requirements, but it can also spotlight opportunities for refining and optimising your tax strategy. This in turn can better serve your financial goals, whatever they may be.
Below we’ve put together some information about individual and company tax rates for the 2022-23 and 2023-24 financial years.
Individual tax rates
Income tax is applied to an individual’s taxable income and is payable on all forms of income, including wages, business profits and investment returns. It can also apply to the sale of assets, such as shares or a house. Australia has a progressive tax system, which means the higher your income, the more tax you pay.
The following individual income tax rates apply for both the 2022-23 and 2023-24 financial year:
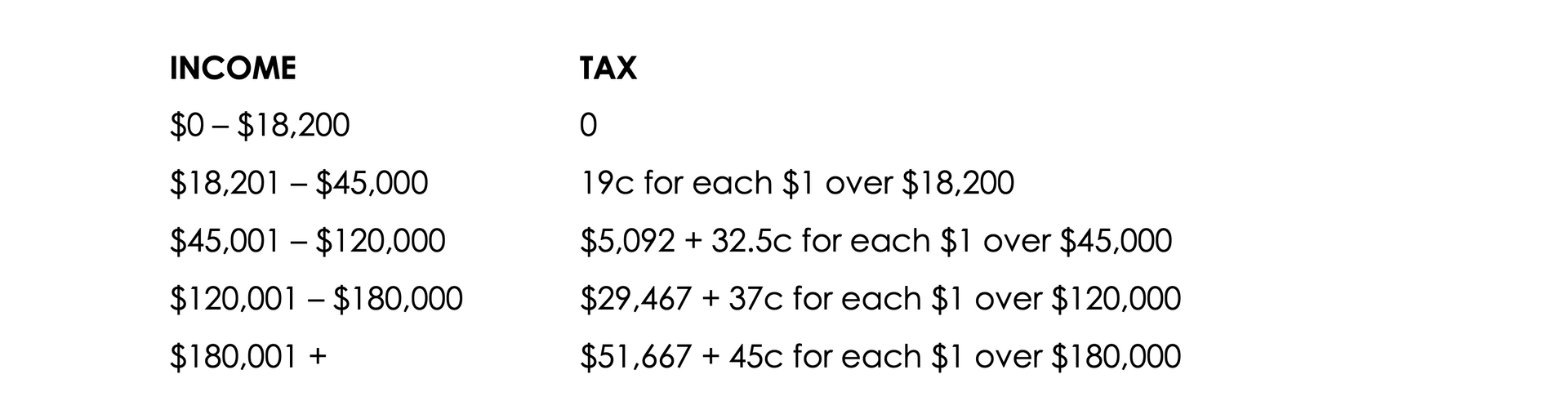
These rates do not include the Medicare levy of 2%.
The tax-free threshold may be higher for eligible taxpayers, e.g. seniors.
Employees generally pay income tax through Pay As You Go (PAYG) withholding, where their employer withholds a portion of their wage each pay period to cover their projected tax liability come June 30.
If you’re a sole trader, your income is considered personal income for tax purposes, meaning you’ll pay the same income tax rate as an individual and only need to lodge one tax return. Similarly, in a partnership, you’ll also pay individual income rates on your share of the partnership income. Both may pay their tax liability via PAYG instalments quarterly, rather than a lump sum at the end of the financial year.
Company tax rates
In Australia, companies are required to pay tax on their earnings. Company (or corporate) tax is a particular rate of income tax that only applies to incorporated businesses. This federal tax is a flat rate, meaning it doesn’t vary based on the amount of income.
The following company tax rates apply for both the 2022-23 and 2023-24 financial year:
Base rate entities 25%
All others 30%
Base rate entities are generally small or medium-sized businesses which fall below the aggregated turnover threshold of $50 million (combined between connected entities).
A company with predominantly passive income cannot access the lower company tax rate. If passive income makes up more than 80% of the company’s total assessable income for the year, they cannot be considered a base rate entity. Passive income includes rent, interest or net capital gains which are earnings not derived from the active operation of a business.
This tax will be applied to the company’s assessable income which is calculated by deducting allowable expenses from total income. It does not include GST collected on sales. As a distinct, legal entity, every company is required to lodge a tax return. Most companies pay this tax liability in quarterly instalments (via PAYG) throughout the year.
Professional tax planning
Gain a professional advantage in your tax preparation with the help of an accountant. Minimise your tax and maximise your benefits with Ascent Accountants. Our experienced accountants are here to help optimise your tax strategy and streamline the preparation process, saving you time, stress and money. Get in touch with our team today to get started.
Need help with your accounting?








